A brief intro to website security.
Enterprises and associations rely heavily on various web applications and platforms for various aspects of their business and their organizations. However, as more and more of their products and services are offered online, they must plan for the increased risk of online security threats. These threats can have far-reaching consequences, including data breaches, financial losses, and damage to personal and operational reputations.
In 2020, data breaches on average cost $3.86 million.
Ponemon Institute’s Cost of a Data Breach Report
To protect your organization from these risks, it’s crucial to be aware of the most common security threats and take proactive measures to address them before they become a major problem.
Threats to keep an eye out for.
Many attacks can happen to enterprises. Be aware of the different types and how you can learn to counteract them.
1. Phishing attacks
Phishing is still one of the biggest threats on the web for most enterprises. Attackers use deceptive emails or websites to trick employees or association members into divulging sensitive information like login credentials, credit card numbers, or other personal details. From there, these attackers can gain access to everything.
How to combat it:
- Training: Regular education and awareness training can help users recognize and avoid phishing attempts.
- Enterprise Software: Upgrading to an enterprise email solution like Google Workspace to leverage built-in spam filtering tools.
2. SQL injection attacks
Most web applications and content management systems, such as WordPress, operate on a Structured Query Language (SQL) database. These databases store and retrieve essential information, from posts to user data like passwords. When an application needs specific data, it runs a command known as a query, often incorporating user inputs such as search terms. For example, a basic SQL query might look like this:
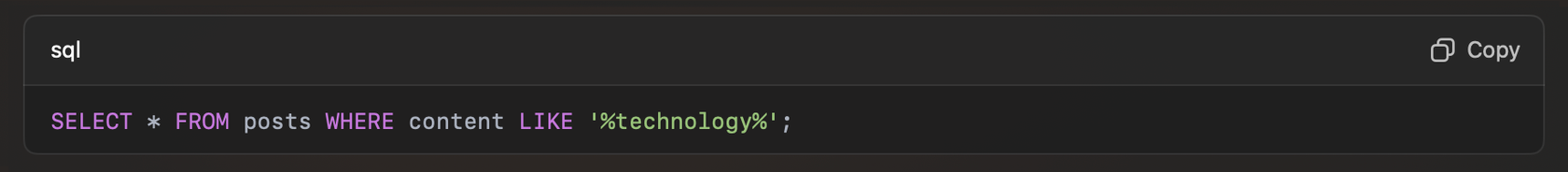
This command retrieves all posts containing the word ‘technology.’
SQL injection attacks exploit these queries’ vulnerabilities by injecting harmful code into user inputs. A hacker might try to manipulate a search field to insert additional commands, effectively altering the query. For example, if a search input isn’t properly sanitized, a hacker could enter something like:
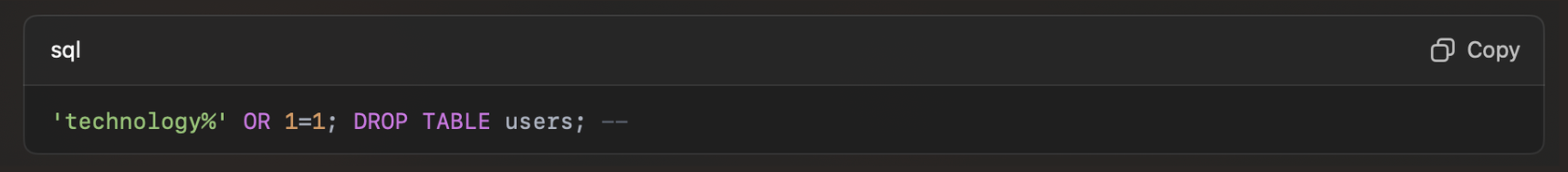
In this case, the query could be transformed into:
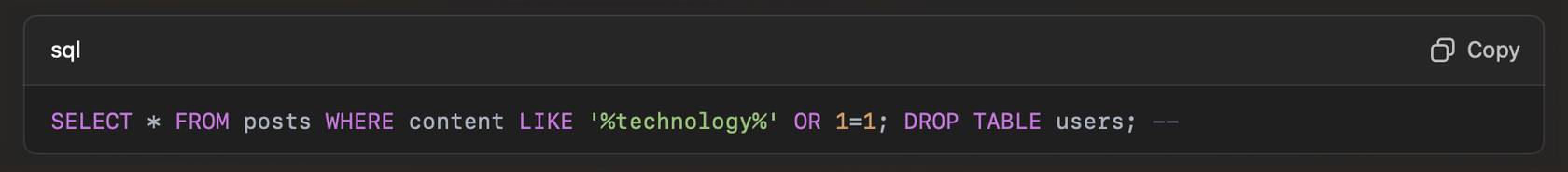
This altered query could have devastating consequences, such as deleting the users’ table, exposing sensitive information, or corrupting data integrity. Although simplified, this example illustrates the potential damage of unsanitized SQL inputs.
How to combat it:
- Valid Data Input Carefully: Implementing strict input validation and parameterized queries are effective defences against SQL injection.
3. XSS attacks
An XSS attack, or Cross-Site Scripting attack, is a type of security vulnerability typically found in web applications. It allows attackers to inject malicious scripts into content that appears to be from a trusted source. This is different from other web attacks, as it does not directly target the application itself but rather exploits a user’s trust in a particular site.
In an XSS attack, the attacker uses a web application to send malicious code, usually a browser-side script, to a different end user. The end user’s browser cannot know that the script should not be trusted and executes it. Since it thinks the script came from a trusted source, the malicious script can access any cookies, session tokens, or other sensitive information retained by the browser and used with that site.
These attacks can be used for various purposes, from stealing credentials or personal information to spreading malware or other malicious activities. Protecting against XSS attacks involves proper data validation and encoding, where user inputs are correctly sanitized before being processed or returned to the application’s output.
How to combat it:
- Use Trusted Third-Party Tools: Ensuring input validation, using security libraries, and regularly updating web application frameworks can help prevent XSS vulnerabilities.
4. DDoS attacks
Distributed Denial of Service attacks overwhelm a website or web service with traffic, rendering it inaccessible to users.
How to combat it:
- Longer TTL: Using dedicated security tools and services to identify and block malicious traffic helps mitigate DDoS attacks. Setting longer TTL can improve cache efficiency and mitigate some of the attacks.
- Content Distribution Networks: Upgrade to a content distribution network or cloud DNS provider such as Fastly or Cloudflare to help mitigate DDoS attacks should they happen.
5. Malware infections
Malware can infect systems through malicious downloads, email attachments, or compromised websites. Once inside, malware can steal data, disrupt operations, or damage systems.
How to combat it:
- Antivirus Software: Antivirus software must be regularly updated, email filters must be employed, and employees and members must be educated on safe browsing practices to prevent malware infections.
6. Credential theft
Attackers often target weak or reused passwords to gain unauthorized access to enterprise accounts. Once inside, there’s no end to what can be stolen or compromised.
How to combat it:
- Password Policies: Implementing strong password policies, enforcing multi-factor authentication, and regularly monitoring accounts for suspicious activity can help prevent credential theft.
7. Zero-day vulnerabilities
Zero-day vulnerabilities are security flaws in software or applications that attackers exploit before developers can release patches. They are especially dangerous because they are unknown to the software’s creators, leaving systems unprotected until a fix is developed.
How to combat it:
- Keep Software and Systems Updated: Regularly update all software and systems to ensure the latest security patches are applied as soon as they’re available. This minimizes the window of opportunity for attackers.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): CDNs like Fastly or Cloudflare offer web application firewalls and threat monitoring to detect and block malicious activity, providing an extra defence against zero-day exploits.
- Deploy Threat Detection and Monitoring Tools: Implement tools that monitor for unusual activity, such as rapid login attempts or unexpected data requests, helping to identify potential zero-day attacks early and limit their impact.
The cost of web security breaches.
Web security breaches have become a familiar and costly threat for organizations worldwide. These incidents encompass a wide range of attacks and can have devastating consequences for organizations.
- Financial consequences: Financial loss is one of web security breaches’ most immediate and tangible impacts. These breaches can result in direct costs such as fines, legal fees, and compensation to affected parties. Indirect costs include system restoration, IT remediation, and loss of business due to downtime.
- Reputation damage: Often, a business’s most significant casualty is its reputation. Customers and stakeholders lose trust in a business that cannot protect sensitive data, and this loss of trust can lead to a loss of clients and revenue. Rebuilding a damaged reputation is a costly and time-consuming process, and some businesses don’t recover.
- Regulatory and legal consequences: Businesses are subject to various data protection regulations, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), which impose strict standards for data security. When a business suffers a web security breach, it can result in regulatory fines and legal actions. Businesses may also be required to notify affected individuals, which can further damage their reputation.
- Operational disruption: Web security breaches can disrupt an association or business’s operations, leading to downtime and decreased productivity. During an attack, a company’s IT team works hard to resolve the issue, diverting resources and attention from regular operations. This disruption can lead to missed opportunities and revenue loss.
- Intellectual property theft: Web security breaches can also result in theft of intellectual property (IP). Businesses invest significant resources in research and development, and the theft of proprietary information can have a long-lasting impact. Stolen IP can be used to create competing products or to harm a company’s competitive advantage.
- Customer churn and acquisition costs: Customer loss due to a breach can be a significant drain on resources, as acquiring new customers can be expensive and time-consuming. Retaining existing customers is much more cost-effective, making customer churn a critical concern for businesses affected by security breaches.
What WebOps can do for you
Our team pushes to be as up-to-date as possible on the latest and safest tech to keep your organization secure. When we build your website, we’re working with plugins we’d use on our website—we research and test to find the most trustworthy and highest-recommended apps to ensure that your site is always running at its best.
We can do that if you want an ongoing WebOps monthly maintenance package. That way, you can focus on what’s important – your organization’s mission – and we’ll keep everything you have online secure, up-to-date, and worry-free.
Stay aware, stay safe.
Security threats continue to grow and evolve, becoming more sophisticated and damaging for websites. Enterprises must remain vigilant and proactive in safeguarding their online assets, and associations must keep their membership and resources secure. Regular training, robust security protocols, and continuous monitoring are critical components of a comprehensive web security strategy.
By staying informed about common threats and proactively addressing them, you can minimize your risk exposure and protect your sensitive data, people, and assets. ct your sensitive data, your people, and your assets.
